
- ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS MANUAL
- ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS FULL
- ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
- ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS CODE
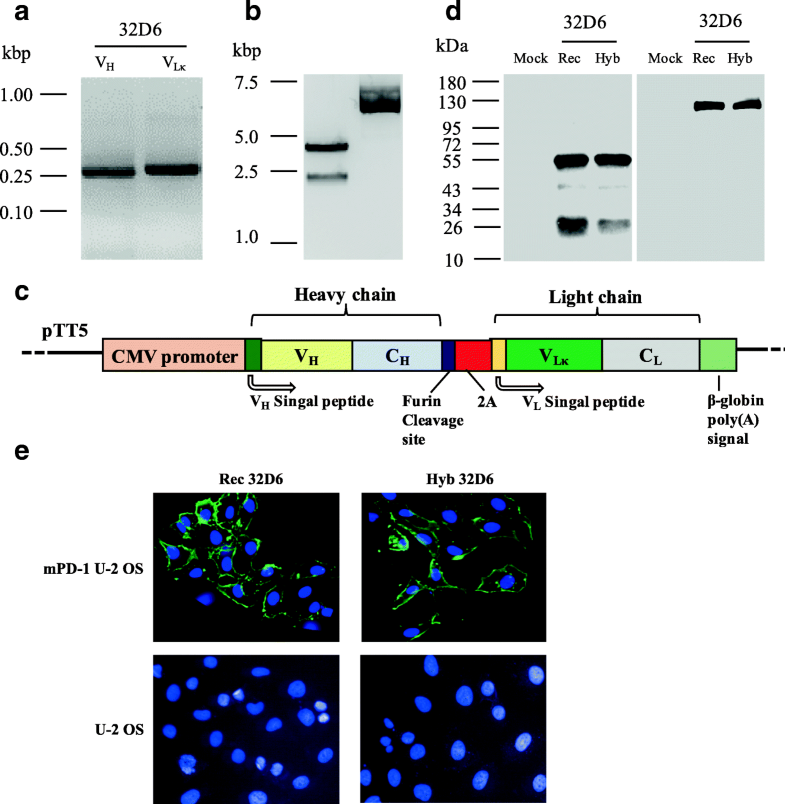
To this end, we identified three requirements for a software-assisted automated cloning pipeline, which are not yet fulfilled by available software solutions: (I) easy-to-access data in a human readable format (II) data processing and cloning recommendations for all analyzed sequences in order to facilitate and optimize cloning efficiency from limited cell numbers, and (III) automated sequence data comparison from cloned plasmid genes to cDNA-derived sequences. We and others therefore focus on the identification and characterization of single mAbs with reactivity against a given auto-antigen. In CSF mAb studies, clonality analysis is less meaningful due to the low number of available cells compared to blood. With the exception of sciReptor, they are not designed to handle single-cell data, therefore Ig heavy and light chain pairing is not preserved, and expression of all cloned antibodies is not possible. These tools are designed to perform clonality analysis of bulk datasets. Thus, protocols require optimization to increase successful expression rates from derived single cells in comparison to bulk approaches from blood samples.Įxisting solutions for antibody sequence data analysis allow high-throughput processing in a database environment and are typically designed to work with next generation sequencing (NGS). As CSF cell samples are challenging to obtain and typically have lower cell counts than samples from other body compartments, recombinant CSF cell cloning is naturally limited. Besides studying disease mechanisms, each CSF-derived mAb can potentially be used for the development of novel diagnostic or therapeutic applications, strongly promoting further investigations of mAb repertoires in a broader spectrum of neuropsychiatric diseases. First CSF cell studies showed direct pathogenic effects of single autoimmune encephalitis patient-derived mAbs in vitro and in vivo, and also indicate local enrichment of disease-specific antibody-producing cells. In neuroscience, applying these approaches to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-derived cells has opened a rapidly developing field: Studying central nervous system mAb repertoires (brain antibody-omics) enables insights into the physiological or pathogenic role of (auto-)antibodies in health and disease. Moreover, recombinant expression approaches can generate libraries of purified mAbs which can be directly used in functional assays and further downstream applications.
ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS FULL
Full repertoire data provide information about genetic composition for each single cell immunoglobulin (Ig), allowing identification of expanded Ig clones and providing insights into restrictions or enrichments of Ig gene usage in B cell populations. Repertoire analysis of patient-derived recombinant monoclonal antibodies (mAb) has become a state-of-the-art approach to investigate B cell (patho-)physiology and assess the role of (auto-)antibodies in disease progression in a variety of autoimmune and infectious diseases.
ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS CODE
BASE can be installed locally or accessed online at Code Ocean. Plasmid sequence identity confirmation by cBASE offers functionality not provided by existing software solutions in the field and will help to reduce time-consuming steps of the monoclonal antibody generation workflow. ConclusionsīASE offers an easy-to-use software solution suitable for complete Ig sequence data analysis and tracking during recombinant mAb cloning from single cells. cBASE automatically concluded expression recommendations in 89.8% of cases, 91.8% of which were identical to manually derived results and none of them were false-positive.
ANTIBODY SEQUENCE ANALYSIS MANUAL
In this case, aBASE yielded correct results in 96% of cases, whereas 4% of cases required manual confirmation. Comparing automated BASE analysis with manual analysis we confirmed the validity of BASE output: identity between manual and automated aBASE analysis was 100% for all outputs, except for immunoglobulin isotype determination. BASE consists of two modules: aBASE for immunological annotations and cloning primer lookup, and cBASE for plasmid sequence identity confirmation before expression. We developed BASE, an easy-to-use software for complete data analysis in single cell immunoglobulin cloning. Current protocols for generation of patient-derived recombinant monoclonal antibody libraries are time-consuming and contain repetitive steps, some of which can be assisted with the help of software automation. Repertoire analysis of patient-derived recombinant monoclonal antibodies is an important tool to study the role of B cells in autoimmune diseases of the human brain and beyond.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
