
If you increase the dimensions of the image, you’ll notice the pixels and the blocks will become much more obvious. Each individual pixel is so small that the image looks clear when you’re seeing it at its intended size. Raster images are made up of many pixels, which are tiny blocks of color. Digital photographs are rasters, as are most images that you see online. You probably see raster files every day, even if you’re not aware of it.
#Raster vs vector image software#
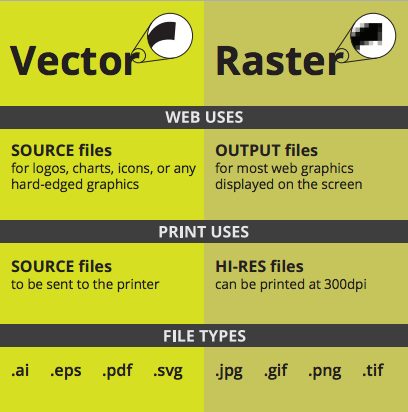
The unlimited scalability is the biggest advantage for vector art in the raster vs vector comparison.Īdditionally, the individual elements of vector files can be edited in software like Adobe Illustrator or Inkscape at any time. The same logo vector file could be used on a small business card or on a huge sign on the side of a building and it would maintain the same clarity with no distortion. For example, logos are created with vectors. As a result, they can have infinite size and resolution. Since they do not consist of pixels, they can be enlarged without distortion or loss of quality. On the other hand, vectors consist of shapes, curves, and paths. As a result, raster graphics will distort or lose sharpness if they are enlarged. Raster files consist of tiny pixels and have a set size and resolution. There are two basic file types: raster (or bitmap) and vector. vector, the details of each, and when they should be used. The width and height attributes in their ‘img’ tags have been set to display them at their proper resolution on the left and at 300 px by 225 px on the right.With many different graphic file types available, choosing the right one is an important part of the design process. In each case below, the images on the left and right are the same. If you attempt to display a small raster image in a size larger than it was created for you will incur pixelization, examples of which are shown below. Raster images that are larger than needed can be ‘scaled’ within an HTML page but each user will still be downloading a larger image file than is necessary. When developing images for the web in a raster format (and when exporting images developed in a vector format into raster), it is important to create a working version that is the right size for your intended display. For this reason you should always develop your graphic at the largest scale you could possibly need it, and then export copies for web display at the actual sizes needed. This means that if you create a great image at 400 pixels wide by 300 pixels high, and then need to display that image at 700 pixels wide, you will lose clarity in the boundaries of elements within your graphic. The thing to remember about raster is that it is not scalable upward.
#Raster vs vector image free#
From expensive software like Adobe PhotoShop or CorelPhoto to free software like Gimp to everyday tools like MS PowerPoint or Paint, we all have experience with raster graphics editors. Much more of your experience in creating images for the web will be with raster graphics editors. On the internet the only common method of displaying an image rendered in a vector style is the new canvas element, an emerging standard in HTML5. Even though your vector-created image is easily and seamlessly exported at 50px and 500px, you will likely display it on the internet as a GIF, PNG or JPG image – all raster file types. For the most part, you will display graphics created with vector editors in a raster format. What vector graphics does not do well is complex shapes and lines that do not follow an easy mathematical formula – ie.
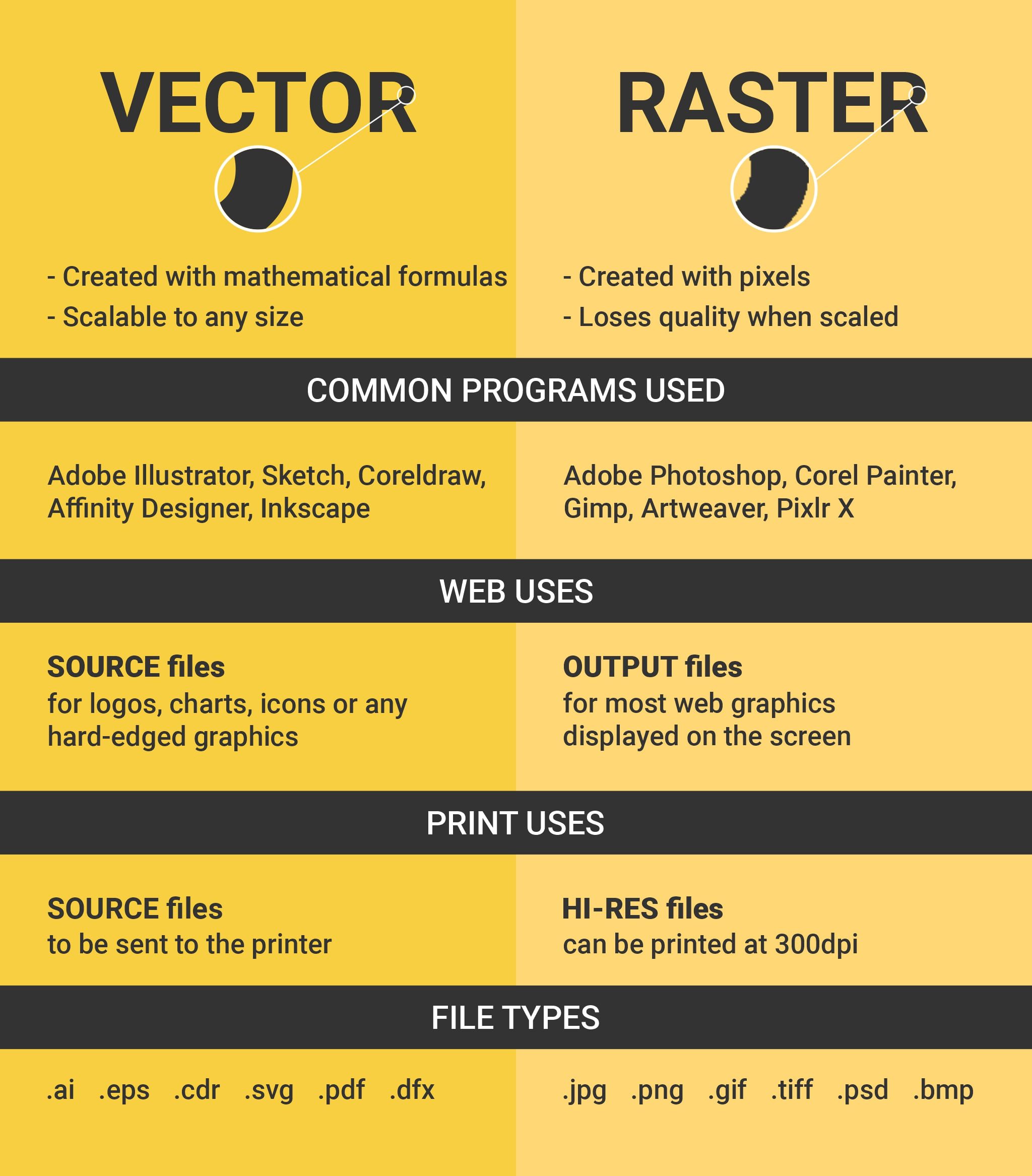
It also means that if you needed to have your graphic on your website (even at different sizes) as well as in print it would be easy to deliver the optimal file for each type of delivery. This means that if you designed an icon, you could reproduce it at different sizes without any change in the sharpness of borders. Vector graphics editors like Adobe Illustrator, CorelDraw and InkScape, allow you to create images in an SVG (scalable vector graphics) format.

Each of these methods of creating graphics have their advantages and disadvantages. In raster editors the image is defined by the colour and intensity of light to be displayed by each pixel in a defined grid or canvas. In vector graphics editors a line or shape is described by the mathematical formulas that define it along with associated data on colour and opacity. In creating graphics there are two types of composition that graphics editors utilize: vector and raster.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
